Physical Water
A physical water is a cuboid shaped area inside which water interaction effects are simulated. The physical water is usually used with water objects: you can add the physical water node together with a water node to indicate an area where physical interactions will take place. Note, however, that you cannot simulate waves by using the physical water.
Bodies with different physical properties behave differently in the same physical water. Therefore, in addition to editing physical water parameters, you should adjust parameters of the physical body in order to get the expected result.
Physical bodies of objects participating in the contact with a physical water can be obtained via UnigineScript. Also you can get the depth of the object submergence, the force applied to the contact, coordinates of the contact point and the relative velocity between the object and the physical water.
By using the physical water, you can create, for example, flows in the ocean.
See also
- A PhysicalWater class to edit physical water nodes via UnigineScript
- A set of samples located in the data/samples/physicals folder:
- water_00
- water_01
Adding Physical Water
To add a physical water to the scene via UnigineEditor:
- Run UnigineEditor.
- On the Menu bar, click Create -> Effect -> Physical Water.

- Click somewhere in the world to place the physical water.

The new physical water node will be added to UnigineEditor and you will be able to edit it via the Nodes panel. By default, the size of the node is 1×1×1 unit.
Editing Physical Water
On the Water tab of the Nodes panel, you can adjust the following parameters of the physical water:
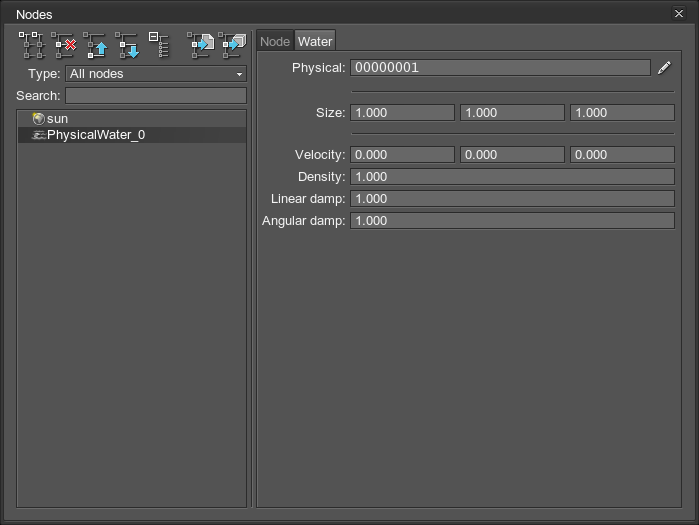
| Physical | Physical mask. The physical mask of the physical water must match the physical mask of the physical object. Otherwise, the physical water won't affect the object. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Size | Size of the physical water box along the axes in units. | ||||
| Velocity | Velocity of the flow in the physical water along the axes. | ||||
| Density | Density of the physical water. It determines buoyancy of objects that float in the physical water. The higher the value, the higher buoyancy of the object.
The lower the water density, the deeper the object submerges into water.
|
||||
| Linear damp | Value indicating how much the linear velocity of the objects decreases when they get into the physical water. The higher the value is, the lower the linear velocity will be. | ||||
| Angular damp | Value indicating how much the angular velocity of the objects decreases when they get into the physical water. The higher the value is, the lower the angular velocity will be. |

