Light Sources
This section covers types of dynamic light sources and lights-related concepts.
Light Sources#
To create a light source, open the Menu bar and click Create -> Lights.

Light sources provide direct real-time lighting which is used for shading on the Deferred and Forward passes of the Rendering Sequence.
The light's Mode defines the impact of the light source on the light baking process and affects rendering of shadows from it:
- Dynamic light sources provide direct real-time lighting only and are turned off while light baking is being calculated. Such light sources provide dynamic shadows only.
- Static lights sources contribute to baking of indirect lighting and remain enabled all the time providing direct real-time lighting. When baked, such light sources are not to be moved; otherwise, this option can cause lack of physical accuracy registered by the eye. Static light sources are able to provide both cached and mixed shadows.
World Light#
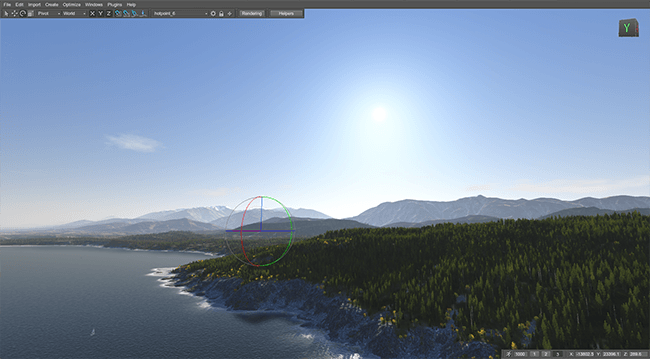
The World Light is an infinitely remote light source casting orthographically projected beams onto the scene. The shadows cast by this light are parallel, which provides a realistic simulation of the light of celestial bodies, such as the Sun and the Moon.
The World Light takes part in the Scattering simulation.
Omni Light#
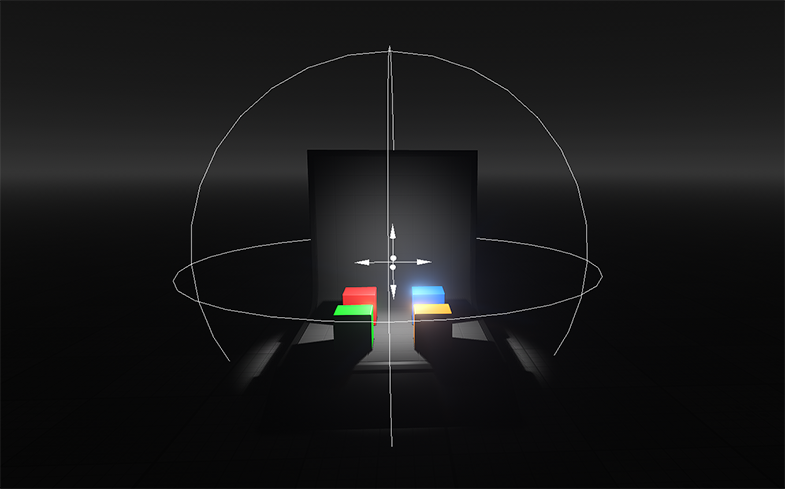
The Omni Light is a point source emitting light in all directions and realistically reproducing shadow cast. This type of light serves to simulate light sources with bright center and equal roll-off of intensity. Omni Light proves useful for general lighting purposes in indoor scenes because of its nondirectional qualities.
Projected Light#
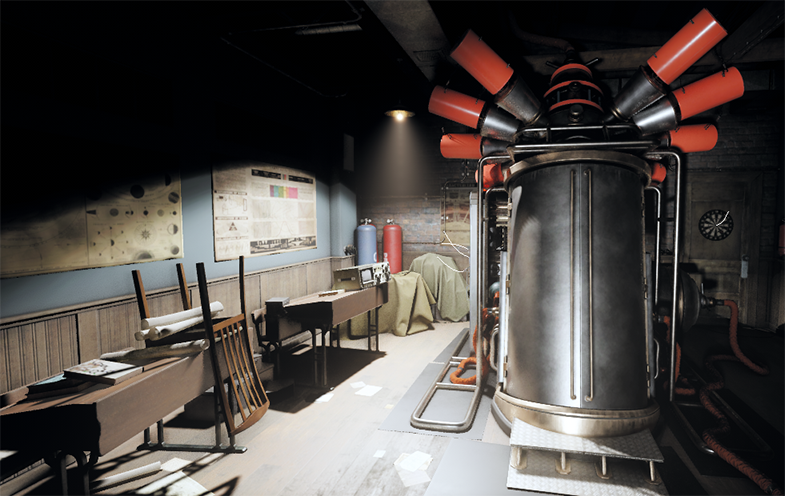

The Projected Light source casts light from a single point forming a focused beam aimed in a specific direction. This type of light is visualized in a form of a pyramid. Due to its form, it is versatile and can be conveniently used to simulate the numerous light emitting sources: for example, car headlights, flash light, or street lamps.
Area Lights#

By default, light sources are represented by a point that emits lighting. Both Omni and Projected light sources have the Shape settings intended to define the shape of an area light source. Area light sources provide wider light spots and correct specular highlights on geometry.
The following shapes are available:
- Sphere
- Capsule
- Rectangle
Lighting Transparent Objects#
Non-opaque geometry is shaded on the Forward pass of the Rendering Sequence. Since all light sources are applied to each transparent surface in a cycle, it is highly recommended to keep the number of lights affecting transparent objects as low as possible for optimal performance.
Global Lights Settings include Forward Per-Object Limits where you can limit the number of certain light sources that affect each transparent object at a time.

Emissive Objects#

The mesh_base and decal_base materials has support for the Emission feature, so any geometry can be made a bright surface. However, it will not illuminate the environment, only glow is rendered by default. Lighting from an emissive object can be baked into GI and computed in real time by using Screen-Space GI.
Optimization#
Scissor Test#
All Omni and Projected light sources are subject to a common deferred optimization technique - the Scissor Test: for each light source a scissor rectangle is found to define its bounds and, therefore, the area of its influence. The scissor rectangle defines the render target for the current light source, since everything that falls outside the region is not affected by the light at the current moment.
Enable the Scissors visual helper or use the render_show_scissors 1 console command to enable visualization of the Scissor Test.

Omni light sources with Point shape and shadows disabled are additionally batched in groups defined by the Batching options:

This optimization enables you to engage huge numbers of omni lights with no significant performance drop.

Interleaved Lights Rendering#
In this mode lighting is rendered during the Deferred pass in half resolution (1/4 of all pixels) with subsequent reconstruction of neighboring pixels using the data from previous frames, making it possible to reduce rendering load.

For more details refer to the Interleaved Lights Rendering article.
See Also#
- The Light Sources section.
- The Lights Optimization article.
- Video Tutorial: Lighting.