Smooth Step Node
Description
Assuming that Max value is greater than Min:
- If input is less than Min then a value 0 is returned
- If input value is in the [ Min , Max ] range then a smooth Hermite interpolation value between 0 and 1 is returned.
- If input is greater than Max then a value of 1 is returned.
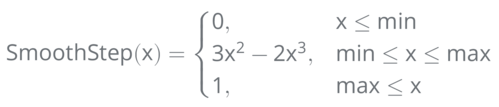
Smooth Step for multi-component data types is applied per-component. If Min and Max have different numbers of components a cast is performed to match the one with the greater number of components.
Simply put, this node converts a linear input gradient to an S-type gradient.
- Min - black input gradient level
- Max - white input gradient level
- Value - input gradient
Usage Examples
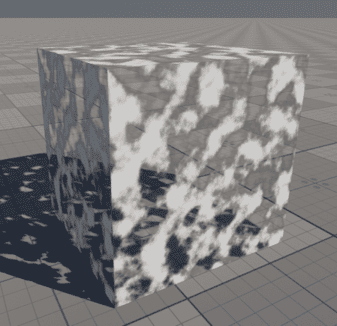
Smooth Dissolving Effect
This material graph demonstrates how to use the Smooth Step node to create a soft mask from a noise texture, with adjustable edge softness. The mask is generated by comparing the noise values against a threshold (fill_percent) with a configurable falloff (diff), producing smooth transitions instead of hard edges.
This smooth mask is then used both for controlling Opacity and blending between black color and the Albedo texture using a Lerp node. The result is a material that dissolves smoothly based on noise-driven masking.
The information on this page is valid for UNIGINE 2.20 SDK.