Матрицы камеры
In UNIGINE, a camera has 2 matrices: the view and projection ones. They are used in rendering of the image from the camera to the viewport.В UNIGINE камера имеет 2 матрицы: view и projection. Они используются при рендеринге изображения с камеры во вьюпорт .
Before getting to the main aspects of the camera matrices, it is necessary to know peculiarities of the coordinate system used by UNIGINE and refresh general knowledge of vector spaces and transformation matrices used for vertex rendering.Прежде чем перейти к основным аспектам матриц камеры, необходимо знать особенности системы координат, используемой в UNIGINE, и освежить общие сведения о векторных пространствах и матрицах преобразования, используемых для визуализации вершин.
Coordinate SystemСистема координат#
The 3D space in UNIGINE is represented by the right-handed Cartesian coordinate system: X and Y axes form a horizontal plane, Z axis points up.Трехмерное пространство в UNIGINE представлено правой декартовой системой координат: оси X и Y образуют горизонтальную плоскость, ось Z направлена вверх.
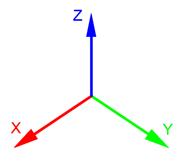
Axes and DirectionsОси и направления#
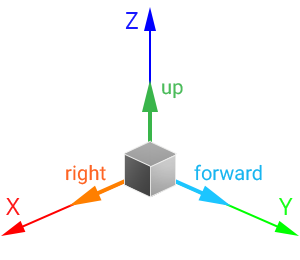
For nodes in the virtual scene: Для узлов в виртуальной сцене:
- The +Z axis is considered the upward direction. To move the node up/down, translate it along the Z axis.Ось +Z считается направлением вверх . Чтобы переместить узел вверх / вниз, перенесите его по оси Z.
- The +Y axis is considered the forward direction. To move the node forward/backward, translate it along the Y axis.Ось +Y считается прямым направлением . Чтобы переместить узел вперед / назад, перенесите его по оси Y.
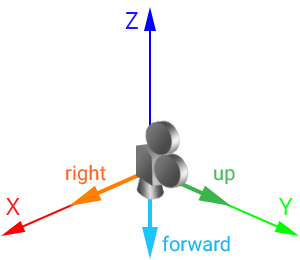
For the virtual camera: Для виртуальной камеры:
- The +Y axis is considered the upward direction.Ось +Y считается направлением вверх .
- The -Z axis is considered the forward direction.Ось -Z считается прямым направлением .
A camera with a default identity transformation matrix looks down:Камера с единичной матрицей преобразования по умолчанию смотрит вниз:
Working with DirectionsРабота с направлениями#
As you can see, direction vectors of nodes and cameras differ. For example, if you need to get the forward direction of the node, you should call the getAxisY() method for its transformation matrix:Как видите, векторы направления узлов и камер различаются. Например, если вам нужно получить прямое направление узла, вы должны вызвать метод getAxisY() для его матрицы преобразования:
// get the node transformation matrix
Mat4 t = node->getWorldTransform();
// get the node "forward" vector from the matrix
vec3 node_forward = t.getAxisY();And if you need to get forward direction of the camera, you should call the -getAxisZ() method for its transformation matrix:И если вам нужно получить прямое направление камеры, вы должны вызвать метод -getAxisZ() для его матрицы преобразования:
// get the inverse modelview matrix as it is equal to the world transformation one
mat4 camera_transform = camera->getIModelview();
// get the camera "forward" vector from the matrix
vec3 camera_forward = -camera_transform.getAxisZ(); // the negative Z vector will be returnedHowever, the camera can be set to a player node. In this case, if you simply call getAxisY() as for any other node, you will get the upward direction of the camera. To avoid this, implement the following:Однако камеру можно установить на узел player . В этом случае, если вы просто вызовете getAxisY(), как и любой другой узел, вы получите направление камеры вверх. Чтобы этого избежать, реализуйте следующее:
// get the node transformation matrix
Mat4 t = node->getWorldTransform();
// get the "forward" vector from the matrix
vec3 forward = vec3(node->isPlayer() ? -t.getAxisZ() : t.getAxisY());Forward direction of the node/camera (if set to the player node) can also be obtained by using the Node::getDirection()/getWorldDirection() method:Прямое направление узла / камеры (при установке на узел player) также можно получить с помощью метода Node::getDirection()/getWorldDirection():
vec3 forward = node->getDirection(node->isPlayer() ? Math::AXIS_NZ : Math::AXIS_Y);Vector Spaces and Transformation MatricesВекторные пространства и матрицы преобразования#
There are the following vector spaces:Существуют следующие векторные пространства:
- Local space is a space in which all vertices of an object are defined relative to the center of this object.Local space - это пространство, в котором все вершины объекта определены относительно центра этого объекта.
- World space is a space in which all vertices of an object are defined relative to the center of the world.World space - это пространство, в котором все вершины объекта определены относительно центра мира.
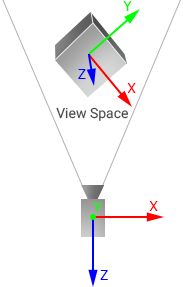
- View space is a space in which all vertices of an object are defined relative to the camera.View space - это пространство, в котором все вершины объекта определены относительно камеры.
- Clip space is a space in which all vertices of an object are defined in a cuboid of [-1;1] dimensions for every axis. The Z coordinate of the vertex specifies how far away the vertex is from the screen.Clip space - это пространство, в котором все вершины объекта определены в кубоиде с размерами [-1;1] для каждой оси. Координата Z вершины указывает, как далеко вершина находится от экрана.
- Screen space is a space in which all vertices of an object are flattened and have screen coordinates.Screen space - это пространство, в котором все вершины объекта сплющены и имеют экранные координаты.
When rendering a vertex, it is transformed from one space into another in the following order:При рендеринге вершина преобразуется из одного пространства в другое в следующем порядке:
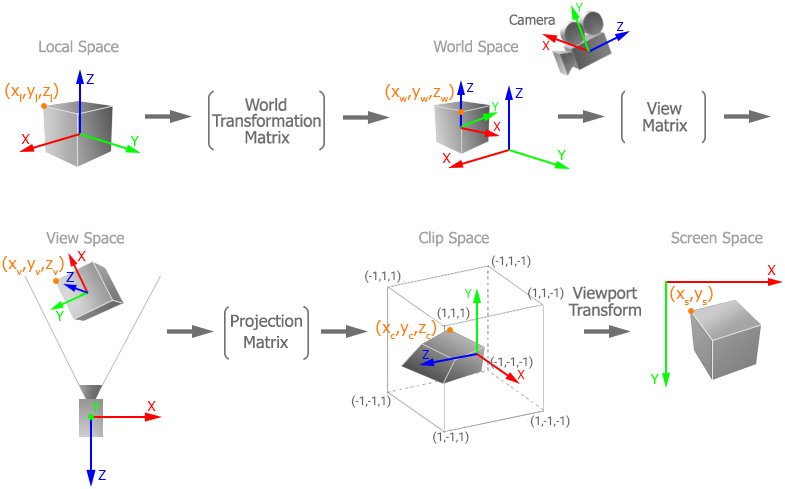
The matrices used to transform between spaces are the following:Для преобразования между пробелами используются следующие матрицы:
-
World Transformation Matrix stores transformation of the object relative to the world origin. This matrix is used to transform the the object's vertices from the local space to the world space: the matrix is multiplied by each vertex of the object.World Transformation Matrix хранит трансформацию объекта относительно начала координат мира. Эта матрица используется для преобразования вершин объекта из локального пространства в мировое пространство: матрица умножается на каждую вершину объекта.
In UNIGINE, such transformation is performed automatically when the node is added into the world. When a node is added into the world as a child of another node, it has also a Local Transformation Matrix that stores transformation of the object relative to its parent. To transform the local transformation matrix of such an object to the world one, the object's local transformation matrix is multiplied by the local transformation matrix of the parent. To get more information about local and world transformation matrices, check the Matrix Hierarchy chapter.В UNIGINE такое преобразование выполняется автоматически при добавлении узла в мир. Когда узел добавляется в мир как дочерний по отношению к другому узлу, он также имеет локальную матрицу преобразования, в которой сохраняется преобразование объекта относительно его родителя. Чтобы преобразовать локальную матрицу преобразования такого объекта в мировую, локальная матрица преобразования объекта умножается на локальную матрицу преобразования родительского объекта. Чтобы получить больше информации о локальных и мировых матрицах трансформации, проверьте Матричная иерархия глава.
-
View Matrix is used to transform the object's vertices from the world space to the view space.View Matrix используется для преобразования вершин объекта из мирового пространства в пространство вида.
ПримечаниеIn UNIGINE, the view matrix is called modelview.В UNIGINE матрица вида называется modelview. - Projection Matrix is used to transform the object's vertices from the view space to the clip space.Projection Matrix используется для преобразования вершин объекта из пространства вида в пространство отсечения.
Each node added into the world has the world transformation matrix. However, passing this matrix to a shader for vertex rendering is unreasonable: it will lead to precision loss because of double to float coordinates conversion. For this reason, in UNIGINE, the node is transformed to the view space first: the product of the world transformation matrix and the view matrix is calculated on CPU and passed to the shader. Such matrix is called Modelview (in its generic meaning).Каждый узел, добавленный в мир, имеет матрицу преобразования мира . Однако передавать эту матрицу шейдеру для рендеринга вершин неразумно: это приведет к потере точности из-за преобразования двойных координат в плавающие. По этой причине в UNIGINE узел сначала преобразуется в пространство представления: произведение матрицы преобразования мира и матрицы представления вычисляется на ЦП и передается шейдеру. Такая матрица называется Modelview (в общем смысле).
Thus, transformation of coordinates of an object's vertex can be represented by the following formula:Таким образом, преобразование координат вершины объекта можно представить следующей формулой:
VertexClip = ProjectionMatrix * ModelviewMatrix * VertexLocalHere the ModelviewMatrix is the product of the world transformation matrix and the view matrix. The order of matrix multiplication is read from right to left.Здесь ModelviewMatrix - это произведение матрицы преобразования мира и матрицы вида. Порядок умножения матриц читается справа налево.
View MatrixМатрица View#
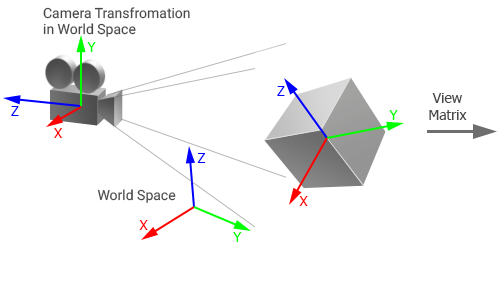
In UNIGINE, the View matrix is the 4x4 matrix that controls the way the camera looks at the scene. The view matrix is equal to the inverse camera world transformation matrix: it stores position and rotation of the camera in world space.В UNIGINE матрица View - это матрица 4x4, которая управляет тем, как камера смотрит на сцену. Матрица вида равна матрице обратного преобразования мира камеры : он хранит положение и поворот камеры в мировом пространстве.
The matrix is used to transform vertices of the object from the world space to the view space (coordinates of vertices are set relative to the camera origin): the camera's view matrix is multiplied by the object's world transformation matrix and then the resulting matrix is multiplied by the object's vertices.Матрица используется для преобразования вершин объекта из мирового пространства в пространство вида (координаты вершин задаются относительно начала координат камеры): матрица вида камеры умножается на матрицу преобразования мира объекта, а затем полученная матрица умножается по вершинам объекта.
 |
 |
Object and camera in world spaceОбъект и камера в мировом пространстве |
Object in view spaceОбъект в поле зрения |
Projection MatrixМатрица Projection#
The Projection matrix is a matrix that defines how vertices are rendered on the screen. The values of the projection matrix depend on the type of projection:Матрица проекции - это матрица, которая определяет, как вершины отображаются на экране. Значения матрицы проекции зависят от типа проекции:
-
For the orthographic projection, the following matrix is used:Для орфографической проекции , используется следующая матрица:
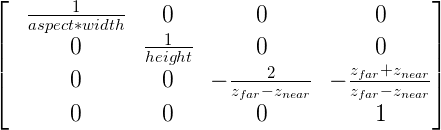
-
For the perspective projection, the following matrix is used:Для перспективной проекции , используется следующая матрица:
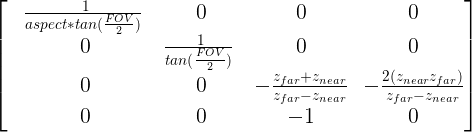
By default, the projection matrix of the camera doesn't store an aspect ratio of the screen (width to height): aspect correction is performed automatically for the current viewport. If manual aspect correction is done, the automatic aspect correction for the viewport must be disabled to avoid incorrect results.По умолчанию матрица проекции камеры не сохраняет соотношение сторон экрана (ширину к высоте): коррекция формата выполняется автоматически для текущего вьюпорта. Если коррекция формата выполняется вручную, автоматическую коррекцию формата для вьюпорта необходимо отключить, чтобы избежать неверных результатов.
If you change FOV (or width and height for orthographic projection), near and far clipping planes, the matrix is updated.Если вы измените FOV (или ширину и высоту для ортогональной проекции), ближнюю и дальнюю плоскости отсечения, матрица обновится.
The projection matrix is used to transform vertices of the object from the view space to the clip space. This space is represented by a cuboid with [-1;1] dimensions for every axis and used for clipping vertices: all vertices inside this volume will be rendered on the screen. In this space, the Z coordinate of each vertex specifies how far away a vertex is from the screen.Матрица проекции используется для преобразования вершин объекта из view space в clip space. Это пространство представлено кубоидом с размерами [-1;1] для каждой оси и используется для отсечения вершин: все вершины внутри этого объема будут отображаться на экране. В этом пространстве координата Z каждой вершины указывает, как далеко вершина находится от экрана.
Then the vertex coordinates in the clip space are automatically transformed to normalized device coordinates by using perspective division. Mapping these coordinates to the screen space is performed on GPU by using the viewport transform vector that stores the following:Затем координаты вершин в пространстве клипа автоматически преобразуются в нормализованные координаты устройства с использованием перспективного деления. Сопоставление этих координат с пространством экрана выполняется на графическом процессоре с использованием вектора преобразования вьюпорта, который хранит следующее:
(width, height, 1/width, 1/height)Camera Matrices SimulatorСимулятор матриц камеры#
Take a look at the following spreadsheet to get a full picture of how camera matrices are handled in UNIGINE. It shows the way the World Transformation, View, and Projection matrices affect the coordinates of a vertex which can be used for debug purposes.Взгляните на следующую таблицу, чтобы получить полное представление о том, как матрицы камеры обрабатываются в UNIGINE. Он показывает, как матрицы World Transformation, View и Projection влияют на координаты вершины, которые можно использовать в целях отладки.
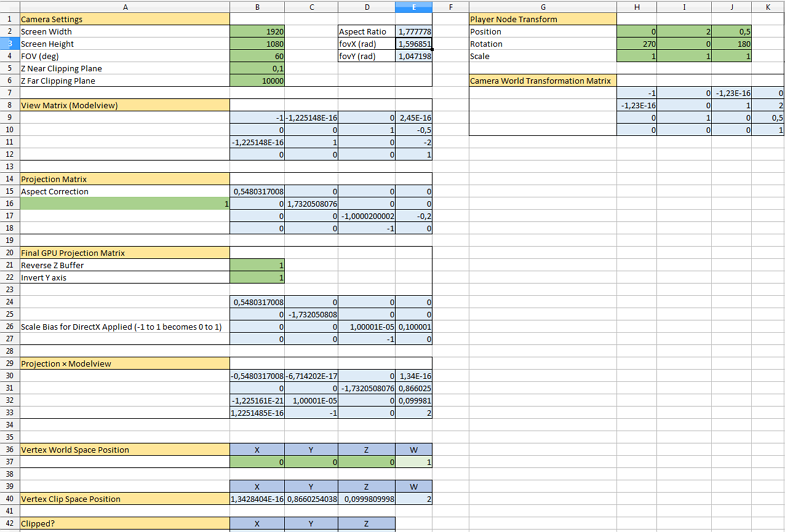
Download the UNIGINE camera matrices simulator.xlsxСкачать UNIGINE camera matrices simulator.xlsx
