Exporting Nodes
Any part of the scene (both a single node or a group of nodes including all children) can be exported from UnigineEditor and saved to a .node, .mesh or .fbx file.
To export a node (or nodes), right-click it in the World Hierarchy window and choose the required menu item:

Exporting Nodes to a NodeReference
Any node (or nodes) from the World Hierarchy can be exported to a node reference. Exporting a node to a node reference may be required, for example, if you want to implement instancing of nodes in your project.
To export a node to a .node file, right-click the target node in the World Hierarchy window and choose Create a NodeReference in the drop-down list.
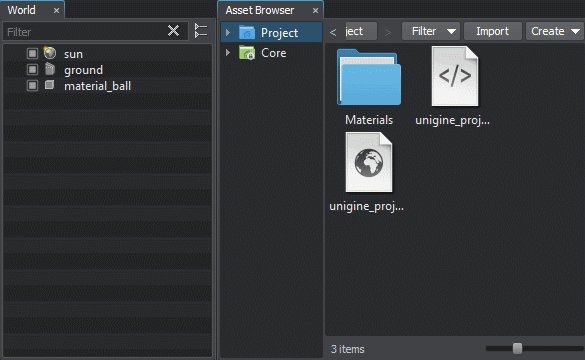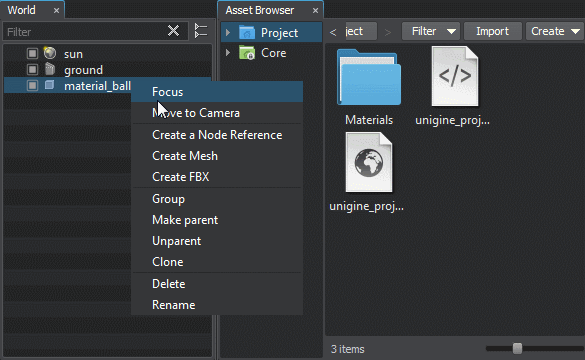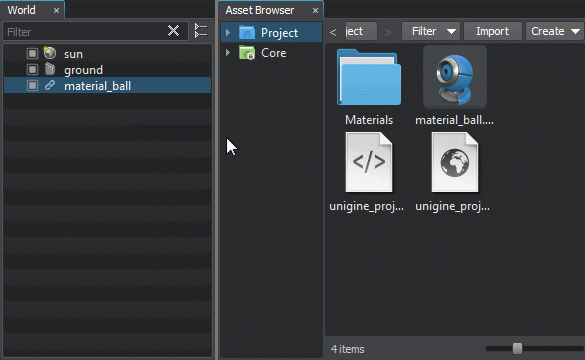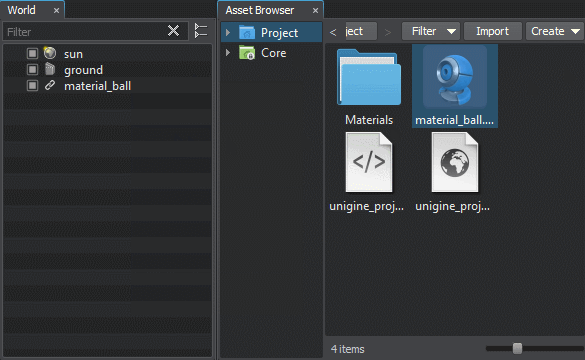
Another way to export a node (nodes) is to select it in any available way and choose Edit -> Convert To NodeReference in the Menu Bar. In both cases, the selected node will be converted to NodeReference, and the .node file named after the node will be created.
If you select several nodes, they will be exported to a single .node file as child nodes of the dummy node.
The exported node will be saved in local coordinates (relative to the zero of coordinates or to the parent node, if any).
Exporting Nodes to a Mesh
Exporting nodes to a mesh may be required, for example, when you have several mesh-based nodes, and you want to get them as a single mesh.
Nodes of the following object-related types can be exported to the .mesh file:
To export a node to a .mesh file, right-click the target node in the World Hierarchy window and choose Create Mesh in the drop-down list.

The exported mesh can be used, for example, to create a mesh-based node.
Exporting Nodes to FBX
Exporting nodes to an .fbx file provides a wide range of use cases for artists: for example, after exporting the scene you can bake lightmaps with the 3rd-party tool (for example, V-Ray).
Nodes of the following types can be exported to the .fbx file:
- Static Mesh
- Skinned Mesh
- Dynamic Mesh
- Node Reference
- All players
- All light sources except Environment Probes
- When exporting a static or dynamic mesh that has more than one surface with the same material, a separate mesh for each surface will be created and saved in the FBX container.
- When exporting a node reference, the node stored by the reference (in the .node file) will be exported.
To export a node to an .fbx file, right-click the target node in the World Hierarchy window and choose Create FBX in the drop-down list.

You can export both a single node or nodes hierarchy tree branch. However, exporting to FBX is available only if one node in the hierarchy is selected. To export the hierarchy tree branch, select and export the parent node: the child nodes will be exported as well. If you need to export the whole scene or its part, the nodes should be added as children to a dummy or layer node in the hierarchy.
The exported node will be saved in local coordinates (relative to the zero of coordinates or to the parent node, if any).
- When exporting a static or dynamic mesh that has more than one surface with the same material, transformation of each created mesh is saved in the parent coordinates. In this case, the parent of the meshes is the static/dynamic mesh that is exported.
- When exporting a node reference, transformation of this node reference is saved rather than transformation of the node stored by the reference.