Vertex UV 1 Node
Description
This node retrieves the second set of UV coordinates from a mesh's vertex data, defining how textures are wrapped around a 3D model and positioned on the mesh. The Vertex UV 1 node is used for sampling textures, for example albedo, normal textures, baked lighting, damage or dirt masks. It is commonly utilized for additional secondary texture layers such as detail maps, decals, or lightmaps.
The Vertex UV 1 node outputs a float2 value representing the UV coordinates stored in the second UV channel.
Use the Vertex UV 0 node to access the first UV set of the UV coordinates.
Usage Examples
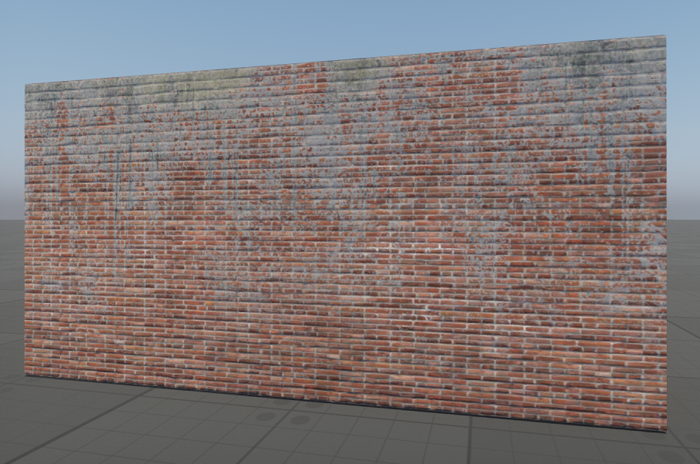
Creating A Brick Wall With Patches Of Dirt
Let's create a brick wall with certain areas covered in dirt.
- First, unwrap the mesh in a 3D editor, ensuring it has two UV sets - one for the brick texture (albedo) and another for the dirt overlay.
- Import the mesh into the editor.
- Use Vertex UV 0 node to map the main brick texture and Vertex UV 1 for the dirt texture.
- Blend them, using the Lerp (linear interpolation) node with the dirt texture's Alpha channel as the blending coefficient.
This setup allows the dirt to appear only in specific areas while preserving the brick texture underneath.
The information on this page is valid for UNIGINE 2.20 SDK.
