Global Physics Settings
The Physics section of the Settings window allows you to adjust global physics-related settings: values set here will be applied to all physical objects in the scene.
Notice
To configure physics settings, open the Settings window by choosing Window -> Settings in the main menu and select Runtime -> World -> Physics section.
For more information on how to add physical properties to objects and set up physical interactions, see the articles in the Physics section.
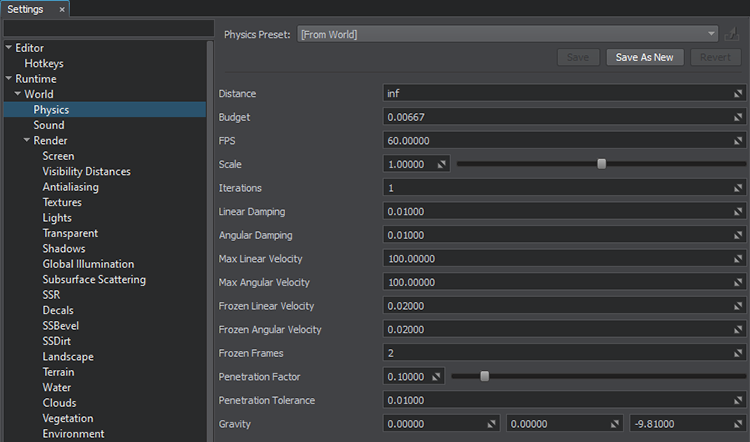
Global Physics Settings Window
The following settings are available:
| Distance | Distance from the camera, from which physical interactions will not be calculated. All physics-based nodes freeze if the distance between them and the camera is bigger than the Physics distance. The distance is measured from the camera to the node's bound.
|
||
|---|---|---|---|
| Budget | Physics simulation time budget in seconds. | ||
| FPS | Fixed frame rate used to simulate physics. Physics frame rate is independent of the rendering one.
Notice
If physics takes more than the assigned time budget, further calculations are delayed. These calculations shall be performed during the subsequent rendering frames, making physics simulation look like in a "slo-mo" mode. The default budget is 50 ms, but it can be increased, as necessary. |
||
| Scale | Scale factor to speed up or slow down the physics simulation time, i.e how frequently physics is simulated (for example, slowing down of body's velocity). Only physics ticks are affected, while everything else is rendered at a normal speed. | ||
| Iterations | The number of iterations for physics during one physics tick. Each iteration the full cycle of physics simulation is performed:
Notice
High number of iterations increases stability, but also results in a higher load. If physics takes more than set in the time budget, next iterations are automatically delayed and moved to the next rendering frame. |
||
| Linear damp | Damping of objects' linear velocities. This value is added to the linear damping set individually for each object.
|
||
| Angular damp | Damping of objects' angular velocities. This value is added to the angular damping set individually for each object.
|
||
| Max linear velocity | The maximum possible linear velocity.
|
||
| Max angular velocity | The maximum possible angular velocity.
|
||
| Frozen linear velocity | Linear velocity at which the object becomes frozen, if it keeps both of its velocities (angular and linear) lower than the freeze velocities.
|
||
| Frozen angular velocity | Angular velocity at which the object becomes frozen, if it keeps both of its velocities (angular and linear) lower than the freeze velocities.
|
||
| Frozen frames | The number of frames, during which an object should keep both its angular and linear velocities under the specified level to become frozen. | ||
| Penetration factor | The factor used to define the rebounding force in case of penetration.
|
||
| Penetration tolerance | Distance in units indicating how deep one object can penetrate another to be rebounded. | ||
| Gravity | Three coordinates of the vector used to define a gravity. It creates a world-wide uniform force field. Gravity is applied at the center of mass of each body (except for dummy body) to calculate its acceleration.
|
Watch an overview of the global physics settings in our video tutorial on physics.
Last update:
2021-04-09
Help improve this article
Was this article helpful?
(or select a word/phrase and press Ctrl+Enter)