Rope Body
Rope body enables physical simulation of ropes, cables, wires, etc. Ropes can be pinned to the following types of bodies:Rope物体可以对绳索、电缆、电线等进行物理模拟。绳索可以固定到以下类型的物体上:
To pin a rope to a body so it would hang freely, or tie several bodies, use a Particles joint. The Rope body can be torn as a Cloth body. Rope enhances the realism of simulated environment and saves the time of game artists as it replaces animation. However, simulation of this type of body is quite costly and it is strongly recommended to use distance optimization to avoid performance hits.要将绳索固定到物体上使其自由悬挂,或将多个物体绑在一起,请使用 Particles联合。Rope物体可以撕成 Cloth物体。绳索增强了模拟环境的真实感,并在替代动画时节省了游戏美术师的时间。但是,这种类型的物体的模拟成本相当高,强烈建议使用距离优化以避免性能下降。
See also也可以看看#
- BodyRope classBodyRope类
- An example illustrating the use of Rope body and Particles joint一个说明 Rope物体和 Particles联合使用的例子
- Fragment of the video tutorial on physics illustrating simulation of wires and ropes using Rope body的片段物理视频教程说明使用 Rope物体模拟电线和绳索
Mesh Requirements网格要求#
The only acceptable mesh type for a Rope body is a cylinder. You can use a standard primitive cylinder to create a rope. The workflow in this case is as follows:Rope物体唯一可接受的网格类型是圆柱体。您可以使用标准的原始圆柱体来创建绳索。本案例的流程如下:
- On the Menu bar, click Create -> Primitive -> Cylinder.在菜单栏中单击 Create -> Primitive -> Cylinder。
-
Specify desired rope parameters (length, radius) for a cylinder, e.g. the following:为圆柱体指定所需的绳索参数(长度,半径),例如:
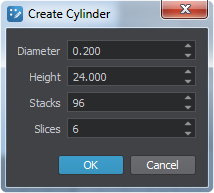
- Click OK and place the cylinder somewhere in the world. It is created as a Static Mesh object. The object itself can be deleted, its mesh however is still available in the data/ folder.点击 OK 并将圆柱体放置在世界的某个地方。它被创建为一个 静态网格 对象。对象本身可以被删除,但是它的网格仍然在 data/ 件夹中可用。
- Create a Dynamic Mesh object and use the cylinder mesh for it.创建一个动态网格 对象,并使用圆柱体网格。
- Assign the rope body to the created dynamic mesh object.将绳子体分配 给创建的动态网格对象。
Mass-Spring Simulation Model质量弹簧仿真模型#
A Rope body is modeled as set of point masses (particles) located in the mesh vertices. Each particle is represented with a sphere shape and is linked together with other particles by inner spring joints that are located along the mesh edges. Inner joints allow to recreate mesh topology, on the one hand, and constrain stretching and folding, on the other.Rope物体被建模为位于网格顶点的一组点质量(粒子)。每个粒子都用球体形状表示,并通过位于网格边缘的内部弹簧接头与其他粒子连接在一起。一方面,内部关节允许重新创建网格拓扑,另一方面可以限制拉伸和折叠。
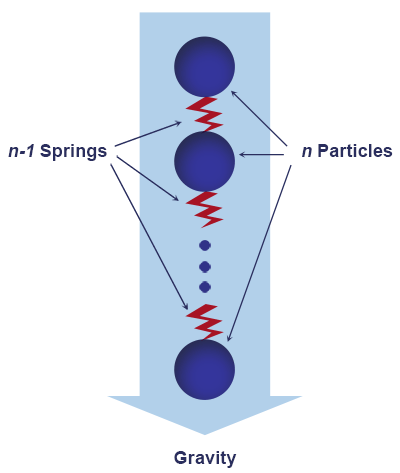
Each particle is characterized by a position, mass and velocity and has a constant spherical shape with a set radius. The total mass of the whole body is equally distributed among them. In accordance with Newton's second law particles can be acted upon by a force or an impulse applied by inner joints and external forces (collision, gravity, air resistance, wind, etc.).每个粒子都以位置、质量和速度为特征,并具有恒定的球形,并具有一组半径.总数大量的全身的能量在他们中间平均分布。根据牛顿第二定律,粒子可以通过力量或冲动由内关节和外力施加(碰撞,重力、空气阻力、风力等)。
Self-collision of the particles and collisions between different rope bodies are not calculated. However, the rope interacts with environment by colliding with other physical bodies if the Collision box is checked. Its behavior in case of contact is controlled by such parameters as friction and restitution. Selective physical interaction is available via corresponding bitmasks.不计算粒子的自碰撞和不同绳体之间的碰撞。但是,如果选中 Collision 框,绳索会通过与其他物理物体碰撞来与环境相互作用。它在接触情况下的行为由以下参数控制摩擦和归还.选择性的物理交互可通过相应的位掩码.
Thus, Rope body can be regarded as a constrained system of rigid particles and therefore shares some parameters with Rigid body:因此,Rope物体可以被视为刚性粒子的约束系统,因此与Rigid物体共享一些参数:
Particle Radius粒子半径#
As already mentioned, each particle is a sphere with a set radius. Thus, particles use continuous collision detection. The rope never lies flat on the ground or tightly adheres to the surfaces. There is always a gap equal to particle radius.正如已经提到的,每个粒子都是一个具有设定半径的球体。因此,粒子使用连续碰撞检测.绳子永远不会平放在地上或紧紧地粘在表面上。总是有一个等于粒子半径的间隙。
As collisions between the particles are not calculated, they should not be considered when setting a radius:由于不计算粒子之间的碰撞,因此在设置半径时不应考虑它们:
- Higher values are preferable for more robust behavior. However, too big radius may result in incorrect interaction with the environment (twitching or blowing up of the rope).对于更稳健的行为,更高的值更可取。但是,太大的半径可能会导致与环境的不正确交互(绳索抽搐或炸毁)。
- Lower values decrease the gap between the Rope body and the surface. However, too low radius results in poor collision handling.较低的值会减少 Rope物体和表面之间的间隙。但是,半径太小会导致碰撞处理不佳。
Joints Solver Iterations关节求解器迭代#
The number of iterations controls the accuracy of the solution of rope inner joints. This number indicates how many times the joints are solved per physics frame. Joints are solved in a random order to provide more predictable stretching results.迭代次数控制着绳内节解的精度。此数字表示每个关节求解的次数物理框架.关节以随机顺序求解,以提供更可预测的拉伸结果。
- Low number of iterations results in faster simulation. However, in this case the rope is more prone to stretching and looks more elastic. The minimum value is 1.迭代次数少可加快模拟速度。然而,在这种情况下,绳子更容易拉伸,看起来更有弹性。最小值为 1。
-
High number of iterations provides more accurate solution of constraints. In this case the rope looks stiffer. The maximum value is 16.大量的迭代提供了更准确的约束解决方案。在这种情况下,绳子看起来更硬。最大值为 16。
注意Increased number of iterations is considerably expensive and at some point ceases to bring a noticeable benefit, so it should be kept within a reasonable cost-effectiveness limit.增加迭代次数是相当昂贵的,并且在某些时候不再带来明显的好处,因此应将其保持在合理的成本效益范围内。
Increasing the number of iterations may help to avoid twitching of a rope.增加迭代次数可能有助于避免绳索抽搐。
Stretching and Folding拉伸和折叠#
A rope may be deformed by stretching and folding. These deformations are controlled with joint constraints of two types:绳索可能会因拉伸和折叠而变形。这些变形由两种类型的关节约束控制:
- Linear restitution controls stretching.线性恢复控制拉伸。
- Angular restitution controls folding.角度恢复控制折叠。
With these types of constraints, it is possible to obtain the desired look and feel of the rope and simulate a variety of different deformable materials ranging from a stiff metal wire to an elastic rubber cord.通过这些类型的约束,可以获得所需的绳索外观和感觉,并模拟各种不同的可变形材质,从硬金属线到弹性橡胶绳。
Linear Restitution线性恢复#
Linear restitution determines how far the rope particles can be stretched apart from each other. It enforces rope joints to restore the distance that was between the vertices of the original mesh:线性恢复决定了绳子粒子可以相互拉开多远。它强制使用绳索接头来恢复原始网格顶点之间的距离:
- By the maximum value of 1, the particles spring back with great force and the rope is hard to stretch. It gives the effect of stiff non-stretch rope, e.g. a metal wire.到1的最大值,粒子回弹力很大,绳子很难拉伸。它提供了坚硬的非拉伸绳索的效果,例如金属丝。
-
The lower the value, the easier the particles are moved away from each other and the more stretchable and elastic the rope is, e.g. a rubber cord.该值越低,颗粒越容易彼此远离并且绳索的可拉伸性和弹性越大,例如橡胶绳。
注意0 and near zero values are not allowed because they cause unstable simulation and blowing up of the rope.0 和接近零的值是不允许的,因为它们会导致模拟不稳定和绳子爆炸。
Angular Restitution角度恢复#
Angular restitution determines the possible angle between rope triangles that are formed by particles. It constrains the folding of the rope by enforcing joints to keep the angle between the triangles of the original mesh:角度恢复决定了由粒子形成的绳索三角形之间可能的角度。它通过强制关节保持原始网格的三角形之间的角度来约束绳索的折叠:
-
By the maximum value of 1, the angles tend to be retained and the rope resists folding. The rope appears to be stiff.通过 1 的最大值,角度趋于保持并且绳索抵抗折叠。绳子看起来很硬。
注意The maximum value may provide unsteady behavior.最大值可能会提供不稳定的行为。 - By the minimum value of 0, the rope can be easily folded and bent in any direction, regardless of the original topology of the mesh.通过 0 的最小值,无论网格的原始拓扑如何,绳索都可以轻松地向任何方向折叠和弯曲。
If the rope is too stretchy and rubbery, try one of the following:如果绳索太有弹性和弹性,请尝试以下方法之一:
- Set linear restitution to 1.将线性恢复设置为 1。
- Increase the number of joints solver iterations.增加关节求解器的数量迭代.
- Use the mesh with fewer vertices.使用顶点较少的网格。
Rigidity of Motion运动刚性#
The Rigidity parameter is an additional constraint of the rope motion to make it stiffer and more inflexible. For that purpose, linear and angular velocities of each rope particle are corrected according to the total velocities interpolated for all the particles.Rigidity 参数是绳索运动的附加约束,使其更硬和更不灵活。为此,每个绳索粒子的线速度和角速度根据为所有粒子插值的总速度进行校正。
- The minimum value of 0, makes the rope elastic, flexible and easily deformable.0 的最小值,使绳索有弹性、柔韧且容易变形。
- The maximum value of 1, makes the rope stiffer and less prone to deformation.1 的最大值,使绳索更硬,不易变形。
Tearing撕裂#
When the rope is stretched or folded beyond its elastic limit, it tears and shreds into pieces. Tearing is caused by applying the force or collision with a physical body, and depends on the rope stiffness (controlled by linear and angular restitution parameters). The rope is torn only along the edges of rope triangles, splitting mesh vertices and duplicating particles.当绳索被拉伸或折叠超过其弹性极限时,它会撕裂并撕成碎片。撕裂是由施加力或与物理物体碰撞引起的,取决于绳索的刚度(由控制线性和角度恢复参数)。绳索仅沿绳索三角形的边缘撕裂,分裂网格顶点并复制粒子。
Linear Threshold Distance线性阈值距离#
Linear threshold sets the distance limit for stretching the rope. When two particles move away from each other further than this limit, joints that connect them break and a the tear appears.线性阈值设置距离限制伸展绳子。当两个粒子彼此远离的距离超过此限制时,连接它们的关节会断裂并出现撕裂。
- If set to infinity (inf), the rope is stretched without tearing. This value is set by default.如果设置为无穷大 (inf),绳索会被拉伸而不会撕裂。该值是默认设置的。
Angular Threshold Angle角度阈值角度#
Same as linear threshold, angular threshold represents a maximum angle to fold the rope relative to its initial state.与线性阈值相同,角度阈值表示最大角度折叠绳索相对于其初始状态。
-
If set to infinity (inf), the rope is folded without tearing. This value is set by default.如果设置为无穷大 (inf),绳索会折叠而不撕裂。该值是默认设置的。
注意It is recommended to keep the angular threshold lower or equal to 180 degrees.建议保持角度阈值低于或等于 180 度。
Optimizing Simulation优化仿真#
Updating each frame a huge number of objects located far away from the camera that are hardly distinguishable or observed as a mass is a waste of resources.更新每一帧远离相机的大量物体,这些物体几乎无法区分或观察为质量是一种资源浪费。
To improve performance and avoid the excessive load, simulation of the rope can be updated with a reduced framerate. When the player is out of the area specified by the Update Distance Limit, the rope stops to be updated and freezes statically.为了提高性能并避免过度负载,可以对绳索进行模拟更新了降低的帧率.当玩家离开 Update Distance Limit 指定的区域时,绳索停止更新并静态冻结。
The set of frame rates given below enables you to specify how often the rope simulation should be updated when the object is visible, when only its shadow is visible, or when it is not visible at all.下面给出的一组帧速率使您能够指定在对象可见、仅其阴影可见或根本不可见时应更新绳索模拟的频率。
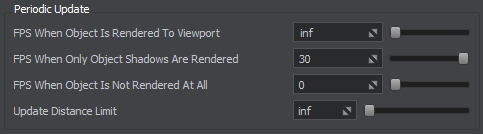
This feature is enabled with default settings ensuring optimum performance and can be adjusted per-object in the UnigineEditor or via API at run time.此功能使用默认设置启用,可确保最佳性能,并且可以在 UnigineEditor 中或通过 API 在运行时针对每个对象进行调整。
Assigning a Rope Body分配绳体#
To assign a Rope body to an object via UnigineEditor perform the following steps:通过将 Rope物体分配给对象统一编辑器执行以下步骤:
- Open the World Hierarchy window.打开 World Hierarchy 窗口。
-
Select a dynamic mesh object to assign a Rope body to.选择一个动态网格要为其分配 Rope物体的对象。
注意Make sure that the object's mesh meets requirements!确保对象的网格满足要求! -
Go to the Physics tab in the Parameters window and assign a physical body to the selected object by selecting Body -> Rope.转到 Parameters 窗口中的 Physics 选项卡并分配一个物理物体通过选择 Body -> Rope 到选定的对象。
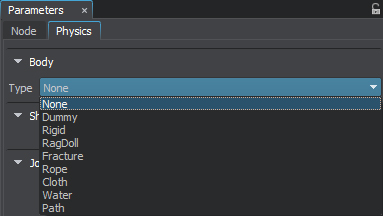
- Set the body's name and change other parameters, if necessary.如有必要,设置物体的名称并更改其他参数。
Attaching a Rope系绳#

Ropes can be attached to the following types of bodies:绳索可以连接到以下类型的物体:
To attach a rope to a body, use the Particles joint. In case of Rigid body (either static or dynamic) and Dummy body, pinned particles stay fixed in their position and follow transformations of attached objects pulling the rope with it.要将绳索连接到物体,请使用 Particles联合。在 Rigid(静态或动态)和 Dummy 物体的情况下,固定粒子保持固定在它们的位置,并跟随用它拉动绳索的附加对象的变换。
- Select Rigid body, RagDoll body or Dummy body.选择 Rigid, RagDoll 或 Dummy物体。
- Add Particles joint.添加 Particles联合。
- Specify Rope body.指定 Rope物体。
- Adjust the pinning area using the Threshold and Size parameters of the Particles joint.使用 Particles联合的 Threshold 和 Size 参数调整固定区域。
Attachment to Skinned Mesh附加到蒙皮网格#
Convincing simulation of the rope on a Mesh Skinned character requires a different approach. To follow bones transformations, each vertex of the rope that is found in the Particles joint area is mapped to the nearest Mesh Skinned vertex (up to the distance specified by the Threshold parameter of the particles joint).令人信服的模拟 Mesh Skinned 角色上的绳索需要不同的方法。为了跟随骨骼变换,在 Particles联合区域中找到的绳索的每个顶点都映射到最近的 Mesh Skinned 顶点(最多由粒子关节的 Threshold 参数指定的距离)。
For example, we need to create a rope that is glued to the hand of a Mesh Skinned character while the rest of the rope hangs and moves loosely. It is done in the following steps:例如,我们需要创建一根绳子,它粘在 Mesh Skinned 角色的手上,而绳子的其余部分则悬垂并松散地移动。它是通过以下步骤完成的:
- When creating a Mesh Skinned, add a rope segment surface identical to the clipped part that needs to be pinned. In our case, it's the rope part in a hand.创建 Mesh Skinned 时,添加与需要固定的剪裁部分相同的绳段表面。在我们的例子中,它是手中的绳索部分。
- Add Mesh Skinned that has a RagDoll body assigned. Make sure that the rope segment surface is enabled.添加 Mesh Skinned 具有RagDoll物体分配的机构。确保启用绳段表面。
- Add a separate dynamic rope mesh and synchronize its position with Mesh Skinned character. Turn off physical simulation (CTRL + SPACE) and assign a Rope body.添加单独的动态绳索网格并将其位置与 Mesh Skinned 角色同步。关闭物理模拟 (CTRL + SPACE) 和分配Rope物体。
- Attach Rope body to RagDoll body. If the Threshold distance of the particles joint is set low enough, the physical rope will be automatically attached only to the rope segment surface (i.e. hand). After that, the rope segment surface is simply disabled and does not provide any load at all.附Rope物体到 RagDoll物体。如果Particles联合的 Threshold 距离设置得足够低,则物理绳索将自动仅附加到绳索段表面(即手)。之后,绳段表面被简单地禁用并且根本不提供任何负载。
本页面上的信息适用于 UNIGINE 2.19 SDK.
