Navigation Sector
A Navigation Sector is a cuboid-shaped navigation area that enables the following:
Both the 2D and 3D routes can be calculated within navigation sectors.
- In case of 2D routes, a point moves in a lower plane of the navigation sector (Z coordinate is not taken into account). If the height or radius set for this point is greater than the size of the navigation sector, such sector is discarded from pathfinding.
- In case of 3D routes, a point moves in three dimensions. If the radius set for this point is greater than the size of the navigation sector, such sector is discarded from pathfinding.
Routes can be calculated within several intersecting navigation sectors. The intersecting sectors are treated as a single navigation area.
NoticeIn case of 2D routes, the height difference between the intersecting sectors must not exceed the maximum height set for the 2D route; otherwise these sectors are discarded from pathfinding.
See also#
- The NavigationSector class to manage navigation sectors via API
- The PathRoute class to create 2D and 3D routes inside navigation sectors
- The article on Creating Routes
A set of samples located in the <UnigineSDK>/data/samples/paths folder:
- route_00
- route_01
- route_02
- sector_00
- sector_01
- sector_02
- Navigation sample in C# Component Samples suite
Creating Navigation Sector#
To create a navigation sector via UnigineEditor:
- Run UnigineEditor.
On the Menu bar, click Create -> Navigation -> Navigation Sector.
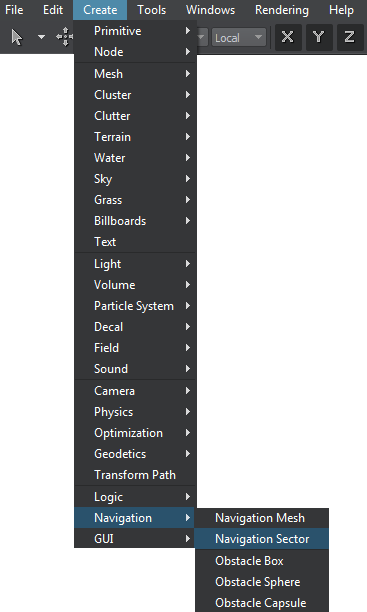
Click somewhere in the world to place the navigation sector.
A navigation sectorA new navigation sector is added to UnigineEditor and you can edit it via the Parameters window.
Editing Navigation Sector#
In the Node tab of the Parameters window, you can adjust the following parameters of the navigation sector:
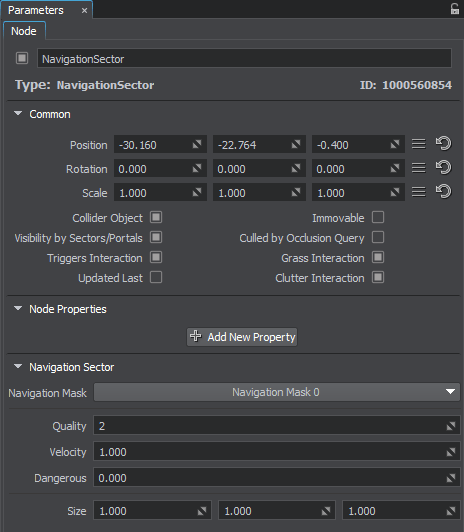
| Navigation Mask | The Navigation mask of the navigation sector must match the Navigation mask of the route that is calculated within it. Otherwise, the sector does not participate in pathfinding. By using the Navigation mask, you can specify sectors that must be ignored during pathfinding. |
|---|---|
| Quality | Quality of optimization for route calculation. This value specifies the number of iterations that are used to find the shortcut. The higher the value, the longer the route calculation will take. |
| Velocity | Scaling factor for velocity of the point that moves inside the navigation sector along the calculated route. |
| Dangerous |
Danger factor that indicates if a moving point should try to avoid the navigation sector. Notice
If the danger factor exceeds the maximum danger factor set for the route, the navigation sector is excluded from pathfinding calculations. |
| Size | Size of the navigation sector's box along the axes. |
The information on this page is valid for UNIGINE 2.19 SDK.