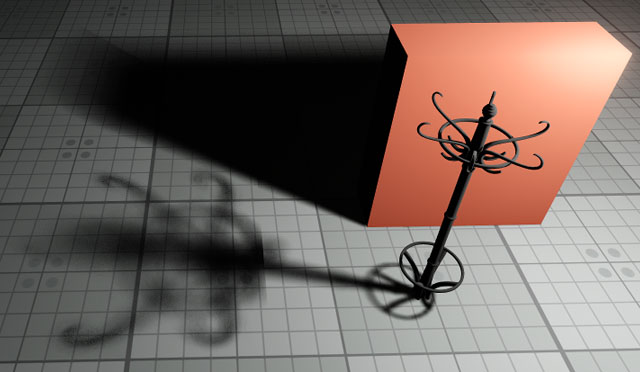
Shadows
UNIGINE provides realtime and precomputed shadows from light sources.
Shadows are cast using a commonly used technique called Shadow Mapping: a depth texture (or a cubemap for omni lights) is grabbed from the position of the light source and used to define lit and shaded areas.
World light sources use an advanced shadow mapping technique called Parallel-Split Shadow Mapping to handle shadows at large distances. The shadow settings are available per each world light source.
To enable shadow casting from a light source, check the Enabled option in its Shadow Settings:
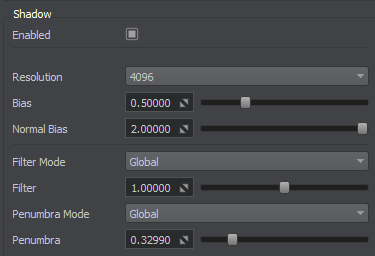
All light sources can be either in Dynamic or Static mode according to which it is decided if shadow maps are computed in real time or saved in an asset once, thus significantly reducing the number of polygons rendered each frame.
Each surface has the shadows-related Rendering Parameters. For a surface to cast shadows, it should have the Cast Proj and Omni Shadows and Cast World Shadows options enabled, the same options are available per material.
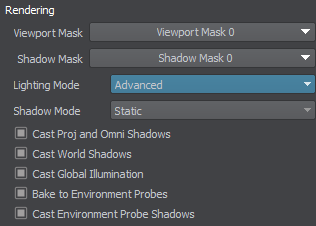
The surface's Shadow Mode is responsible for the type of shadows cast by the surface:
- Static. The surface casts both types of shadows: cached (from static lights) and dynamic (from dynamic lights).
- Dynamic. The surface casts shadow only if lit by a dynamic light or a static light with Mixed shadow mode. No shadows baked.
You can control shadow-related interactions between surfaces/materials and light sources by using the Shadow Mask.
See Also#
- Common Shadow Settings of light sources.
- Global Shadow Settings.
- Video tutorial: Cached Shadows
- Quick video guide: Using Cached Shadows.
Dynamic Shadows#

Dynamic or realtime shadows are useful in changing scenes: when a light source or objects lit by it move. In this case all affected geometry is rendered into shadow buffer one more time, which might affect the performance.
To make a light source provide dynamic shadows, set the Mode to Dynamic and adjust the Shadow Settings.
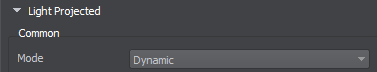
Cached Shadows#
Mostly, virtual environments tend to be static. That is why it makes sense to drop the shadows computation each frame to gain the performance.
The idea behind precomputed Cached Shadows is to grab the shadow map of a light source and save it in an asset to be rendered later at run time.
To get shadows from a light source cached:
- Select Static Shadow Mode for all stationary surfaces. This is the default mode for surfaces of Mesh Static objects.
-
Open Bake Lighting window and check Bake Static Shadows For Lights.
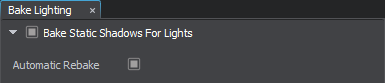 NoticeEnable the Automatic Rebake option to make shadows for static light sources be automatically rebaked every time you make changes to their transformation and shadows-related settings.
NoticeEnable the Automatic Rebake option to make shadows for static light sources be automatically rebaked every time you make changes to their transformation and shadows-related settings. -
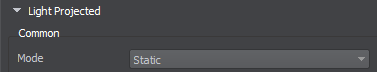
Choose Static Mode for the light source.
-
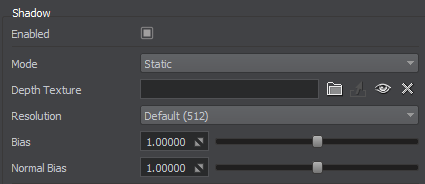
In the Shadow Settings, select the Static shadow mode and Resolution of the shadow map.
- Click Bake Selected in the Bake Lighting window. The shadow map of the light source will be saved at the bake_lighting/shadows folder and assigned to the Depth Texture asset field.
After that, the light source will provide static cached shadows only. After changing light's position, rotation or parameters, it should be rebaked for proper shadow casting.
World light sources require additional adjustments. For more details refer to the Shadow Settings of the World light.
Mixing Dynamic and Cached Shadows#
By using the Mixed shadow mode you can combine baked shadows from static geometry and realtime shadows cast by certain dynamic meshes:
- Select Static Shadow Mode for all stationary surfaces.
- Select Dynamic Shadow Mode for all moving or changing surfaces.
-
Open Bake Lighting window and check Bake Static Shadows For Lights.

-
Choose Static Mode for the light source.

-
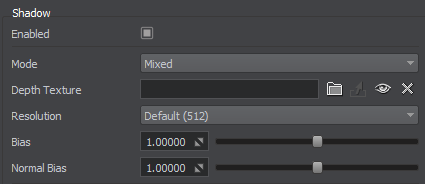
In the Shadow Settings, select the Mixed shadow mode and Resolution of the shadow map.
- Click Bake Selected in the Bake Lighting window to bake static shadows. The shadow map containing shadows cast by static geometry will be saved at the bake_lighting/shadows folder and assigned to the Depth Texture asset field.
After that, the light source will provide both cached and dynamic shadows. After changing light's position, rotation or parameters, it should be rebaked for proper shadow casting.
Area Shadows#
Soft shadows from area lights can be simulated for both static and dynamic light sources by using the Penumbra Settings.
Screen-Space Shadows#
Screen-Space Shadows are raytraced shadows calculated in screen space. This effect does not depend on the polygon count, that is why it may be a great solution for small contact shadows or shadows at a high distance from the camera.
The information on this page is valid for UNIGINE 2.19 SDK.